“China’s Road to the Future: Chip Technology Soars Without Silicon” Imagine a world where the speed and efficiency of modern computing and transportation systems are revolutionized by powerful, yet untested, chip technologies that defy the conventional wisdom of silicon-based components. Welcome to the dawn of a new era, where China is leading the charge to unlock the secrets of the most critical computing infrastructure – and doing it without the familiar constraints of traditional silicon. This is the story of “changing lanes,” a groundbreaking innovation that’s transforming the way China approaches chip technology, from the ground up, and raising fundamental questions about the limits of innovation. As the world watches, China is setting a new benchmark for breakthroughs in computing and transportation, forging a path that could redefine the world as we know it.
Innovation Under Sanctions
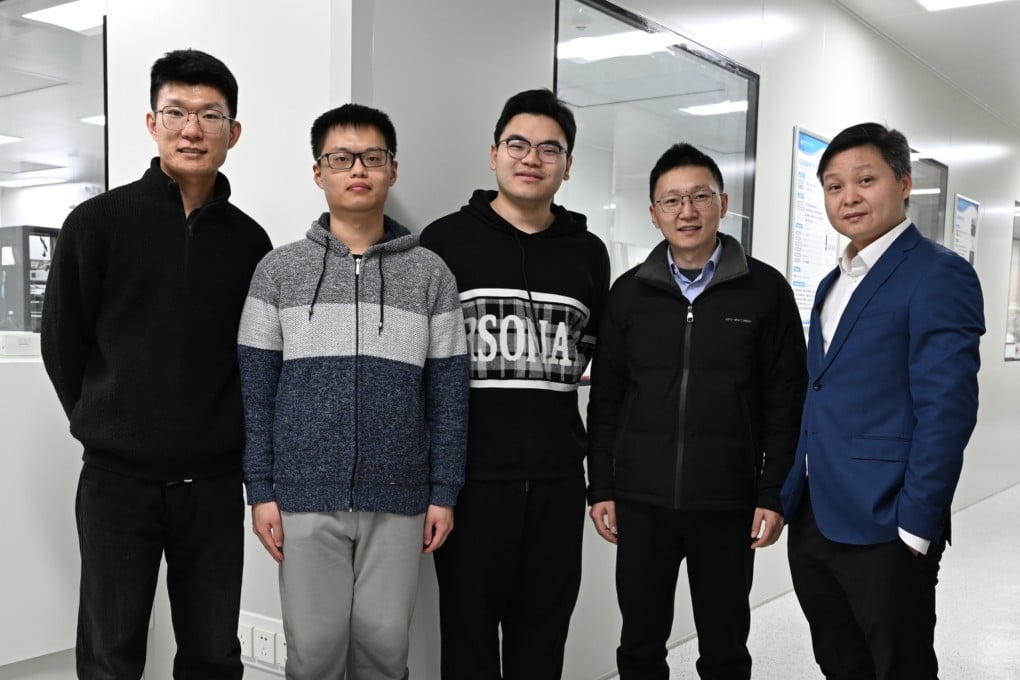
The semiconductor industry is at the heart of global technological advancement, and for years, China faced significant hurdles in this field due to stringent export controls and sanctions. Despite these challenges, a team of researchers at Peking University, led by Professor Peng Hailin, has managed to break through the barriers by developing a 2D bismuth-based transistor. This innovation not only operates 40% faster than the current silicon-based transistors from leading manufacturers like Intel and TSMC but also consumes 10% less energy. The development represents a significant shift in semiconductor technology, moving away from the conventional silicon-based designs to novel materials that can potentially redefine the industry.
Sanctions have played a pivotal role in driving this innovation. The necessity to circumvent silicon-based roadblocks has pushed Chinese researchers to explore alternative materials and designs. This breakthrough, therefore, is a direct response to geopolitical pressures, demonstrating that innovation can indeed arise from necessity. The team’s approach of ‘changing lanes’ from traditional materials to 2D materials opens up new avenues for semiconductor technology, possibly leading to more robust and efficient chips in the future.

Economic Opportunities and Challenges
Economic Implications
The economic implications of this breakthrough are profound for China’s semiconductor industry. The development of a faster and more energy-efficient alternative to silicon-based transistors paves the way for China to potentially reduce its dependency on imported semiconductor technology. This could lead to a significant shift in the global semiconductor market, where China could emerge as a leader by leveraging its proprietary technology. The economic impact is not just limited to the semiconductor industry but extends to sectors that heavily rely on semiconductor technology, such as telecommunications, automotive, and advanced computing.

Challenges Ahead
Despite the promising outlook, there are significant challenges. The transition from silicon to bismuth-based transistors involves retooling existing manufacturing processes and developing new standards. This could be costly and time-consuming. Moreover, the new technology faces the challenge of scaling up production without compromising on quality and performance. Additionally, intellectual property and market acceptance pose significant hurdles, as the industry would need to be convinced of the reliability and long-term viability of bismuth-based transistors.
Future Directions and Potential Applications
Next Steps in Development
Future research and development plans focus on refining the existing bismuth-based transistor technology and expanding its applications. The team at Peking University is looking into optimizing the manufacturing process to make mass production more feasible. They are also exploring the integration of these transistors into existing and emerging technologies, aiming to create a more integrated and cohesive ecosystem for 2D material-based semiconductors. This includes developing more advanced manufacturing tools and testing methods to ensure the robustness and reliability of the new technology.
Potential Applications in Technology
The potential applications of this technology are vast and could revolutionize multiple sectors. In computing, the faster and more energy-efficient transistors could lead to more powerful and efficient processors, enhancing performance across a range of devices from smartphones to supercomputers. In telecommunications, the technology could enable faster data transfer rates and lower power consumption in communication devices, which is crucial for the widespread adoption of 5G and beyond. Furthermore, in the automotive industry, the development could enhance the performance of vehicle electronics, leading to more efficient and reliable autonomous driving systems.
Global Reactions and Responses
International Reactions
The international reaction to the development of the new bismuth-based transistor has been mixed. While some countries and industry experts are cautiously optimistic about the technological leap, others are wary of the implications for global supply chains and intellectual property rights. International bodies like the World Trade Organization (WTO) and the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) are closely monitoring the development, assessing its impact on global standards and trade policies. There is also significant interest from the academic community, with various universities and research institutions conducting independent studies to validate the claims made by the Peking University team.
Collaboration and Competition
From a competitive standpoint, the development has intensified the rivalry in the semiconductor industry. Major semiconductor manufacturers such as Intel, TSMC, and Samsung are now under increased pressure to innovate further and stay ahead in the technology race. On the other hand, the potential for collaboration is also present. As the technology matures, there is a possibility of international partnerships to standardize the new material and integrate it into existing semiconductor manufacturing processes. This could lead to a more collaborative approach to technological advancement, blending the strengths of different regions and expertise.
Environmental and Ethical Considerations
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
One of the critical advantages of the bismuth-based transistor is its environmental impact. Bismuth is a relatively abundant and less toxic material compared to silicon, which requires extensive energy and resource-intensive processes for extraction and manufacturing. This shift could significantly reduce the environmental footprint of semiconductor production, aligning with global sustainability goals. As the world moves towards greener technologies, the adoption of bismuth-based transistors could represent a major step towards more sustainable electronics.
Ethical Implications of Technological Leap
The ethical implications of this technological leap are multifaceted. On one hand, it represents a significant leap in technological advancement, potentially closing the technological gap between China and leading semiconductor manufacturers. However, the development also raises questions about the ethical use of technology and its broader societal impact. As with any major technological breakthrough, there is a need to ensure that the development and deployment of this technology are guided by ethical considerations. This includes addressing issues related to data privacy, cybersecurity, and equitable access to these advanced technologies across different regions and communities.
Conclusion
Revolutionizing the Semiconductor Industry: China’s Breakthrough in Chip Technology
In a groundbreaking development, China has made history by unveiling the fastest-ever chip technology that defies the conventional use of silicon. As reported by the South China Morning Post, this pioneering achievement has sent shockwaves throughout the global tech community, sparking both excitement and concern. At its core, the article highlights the key points that China’s researchers have successfully developed a semiconductor chip using a novel material, marking a significant departure from the traditional silicon-based technology. This innovation not only underscores China’s commitment to driving technological advancements but also underscores the country’s growing presence in the highly competitive semiconductor industry.
The implications of this breakthrough are far-reaching and profound. As the world’s most populous country, China’s dominance in the chip technology sector has the potential to reshape the global economy, with far-reaching consequences for industries ranging from electronics to automotive. Moreover, this achievement underscores the country’s growing capabilities in cutting-edge research and development, positioning it as a major player in the high-tech arena. As the semiconductor industry continues to evolve at breakneck speed, China’s leadership in this field will undoubtedly have a lasting impact on the global landscape.
As we look to the future, it is clear that China’s groundbreaking chip technology will revolutionize the way we think about computing and innovation. With the rapid proliferation of 5G networks, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT), the demand for high-performance chips will only continue to escalate. China’s leadership in this space will enable the country to drive the next wave of technological advancements, transforming industries and transforming lives. As the world hurtles towards a new era of technological progress, one thing is certain: China’s pioneering spirit and innovative prowess will be at the forefront of this revolution, shaping the course of history for generations to come.