In a move that could reverberate throughout the tech industry, the Trump administration has made a strategic decision to exempt a select group of electronics from China tariffs. The announcement, which has sent shockwaves through the stock market, is expected to have a significant impact on the fortunes of two prominent American companies: Apple and Nvidia. As trade tensions between the US and China continue to simmer, this unexpected development has the potential to breathe new life into the portfolios of these two tech giants. But what does this mean for investors, and how will this shift in policy affect the global electronics market? In this article, we’ll explore the implications of this exemption and what it could mean for the future of technology.
Shifting Semiconductor Landscape
US and Netherlands Policy Changes

Biden’s new regulatory framework for the responsible diffusion of advanced artificial intelligence technology marks a significant development in the semiconductor industry. The Department of Commerce’s Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) announced controls on advanced computing chips and certain closed artificial intelligence (AI) model weights. According to the announcement, this new regulation serves key U.S. national security and foreign policy interests and supports the Biden-Harris Administration’s broader strategy to cultivate a secure and trusted technology ecosystem for the responsible use and diffusion of AI. U.S. Secretary of Commerce Gina Raimondo stated, “Managing these very real national security risks requires taking into account the evolution of AI technology, the capabilities of our adversaries, and the desire of our allies to share in the benefits of this technology. We’ve done that with this rule, and it will help safeguard the most advanced AI technology and help ensure it stays out of the hands of our foreign adversaries, while we continue to broadly share the benefits with partner countries.”
However, recent moves by President Trump have introduced an element of unpredictability. Trump’s administration has signaled intentions to rescind President Biden’s executive order regulating AI, which previously required AI companies to share safety test results and critical information with the federal government. While this move could lead to less stringent regulations, it also opens the door for new policies that could shape the AI landscape differently. President Trump has criticized Biden’s AI regulations, arguing that they hinder tech innovation. The implications of these changes are yet to be fully realized, but they are expected to influence the global semiconductor market significantly.
In the Netherlands, the government has announced plans to modify its national export control measures for advanced semiconductor manufacturing equipment exports. Effective from April 1st, 2025, these new policies will limit the export of specific measuring and inspection equipment used in producing advanced semiconductors. Netherlands Minister of Foreign Trade and Development, Reinette Klever, emphasized the importance of maintaining a strategic balance, stating, “We believe it is important to maintain control without stifling technological development.”

Implications for Global Supply Chain
The long-term effects of these policy changes on the semiconductor industry will likely be profound. The global semiconductor supply chain is poised for significant restructuring, as countries like the United States and the Netherlands tighten their export controls and implement new regulations. These changes are expected to reshape the global technology landscape, with companies and governments adapting to new trade policies and regulatory environments.
Companies like Apple and Nvidia, which heavily rely on semiconductor manufacturing and AI technologies, are particularly affected. Apple, for instance, has been directly impacted by the Trump administration’s tariffs on Chinese imports, which have added substantial costs to their manufacturing processes. The tariffs, including a 104% levy on certain goods, could potentially increase the production costs of the iPhone by up to $350 per unit, according to some analysts. This sudden imposition of tariffs has created uncertainty for Apple, as it seeks to either absorb costs or pass them on to consumers, which could negatively impact its market position.
Nvidia, on the other hand, faces challenges in accessing the advanced semiconductor manufacturing equipment it needs for its high-performance computing and AI applications. The Netherlands’ new export control measures could limit Nvidia’s ability to obtain necessary equipment, potentially slowing down its research and development processes. However, the company is also exploring alternative manufacturing options to mitigate these risks.
Rivalry in Innovation
China’s Rise as an Innovator
The semiconductor industry is witnessing a growing rivalry between Western nations and China, with the latter making significant strides in innovation. The Information Technology and Innovation Foundation (ITIF), with support from the Smith Richardson Foundation, has conducted an analysis showing that while Chinese companies are not yet as innovative as their Western counterparts, they are catching up rapidly. This rapid innovation, coupled with the significant scale of resources allocated by the Chinese government, poses a substantial challenge to Western tech giants.
The Netherlands’ and the U.S.’s export control measures are partly a response to China’s rapid advancements. However, the effectiveness of these measures remains to be seen. China’s strategic investments and government backing have enabled it to develop a robust semiconductor ecosystem, which could potentially render export controls less effective over time. The Netherlands’ new export control policies, while aimed at limiting China’s access to advanced technology, may not entirely halt China’s progress but could slow it down, giving Western companies an opportunity to maintain their competitive edge.
Chinese firms’ ability to innovate and compete on a global scale is a testament to the evolution of China’s economic model. While the country initially relied on low-cost manufacturing, it is now investing heavily in research and development (R&D) to become a global leader in semiconductor technology. This shift is evident in the increasing number of patents and research articles published by Chinese firms, as well as their growing presence in global markets.
Apple and Nvidia’s strategies in response to these policy changes are critical to their long-term success. Apple, for instance, has been working on diversifying its supply chain to reduce dependency on Chinese manufacturing. The company is exploring manufacturing options in countries like Vietnam and India, though the costs associated with these changes are significant. For Nvidia, the focus is on leveraging partnerships with advanced semiconductor manufacturers outside of China to secure the necessary equipment and materials for its operations.
Catching Up with Western Nations

The semiconductor industry is undergoing significant shifts, with critical policy changes in the United States and the Netherlands shaping the trajectory of the global supply chain. These developments highlight how the shifting priorities of new government administrations can then impact the worldwide semiconductor market.
The U.S. and the Netherlands especially have firm grips on specific sectors of the semiconductor supply chain that can significantly affect the countries subjected to these limitations. As these policies take effect, their long-term implications for the global semiconductor supply chain will become more evident. The coming months will determine how these shifts reshape the global technology landscape.
Massive Scale of Efforts and Rapid Growth Rate
According to an article on the announcement, “the Department of Commerce’s Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) announced controls on advanced computing chips and certain closed artificial intelligence (AI) model weights, alongside new license exceptions and updates to the Data Center Validated End User (VEU) authorization.” “This new regulation serves key U.S. national security and foreign policy interests and supports the Biden-Harris Administration’s broader strategy to cultivate a secure and trusted technology ecosystem for the responsible use and diffusion of AI.”
“This policy will help build a trusted technology ecosystem around the world and allow us to protect against the national security risks associated with AI, while ensuring controls do not stifle innovation or US technological leadership,” said U.S. Secretary of Commerce Gina Raimondo. “Managing these very real national security risks requires taking into account the evolution of AI technology, the capabilities of our adversaries, and the desire of our allies to share in the benefits of this technology. We’ve done that with this rule, and it will help safeguard the most advanced AI technology and help ensure it stays out of the hands of our foreign adversaries, while we continue to broadly share the benefits with partner countries.”
Consequences for Western Companies
Threat to Technology-Based Companies and Capabilities
The need for robust innovation to maintain a lead is more pressing than ever for Western companies, particularly in the technology sector. The rapid growth rate of China’s innovation efforts poses a significant threat to Western companies and their capabilities.
Need for Robust Innovation to Maintain Lead
Western companies must innovate at a rapid pace to maintain their competitive edge. The stakes are high, and the consequences of not keeping up with the pace of innovation could be severe.
Tariff Exemptions and Their Impact
Apple and Nvidia to Benefit
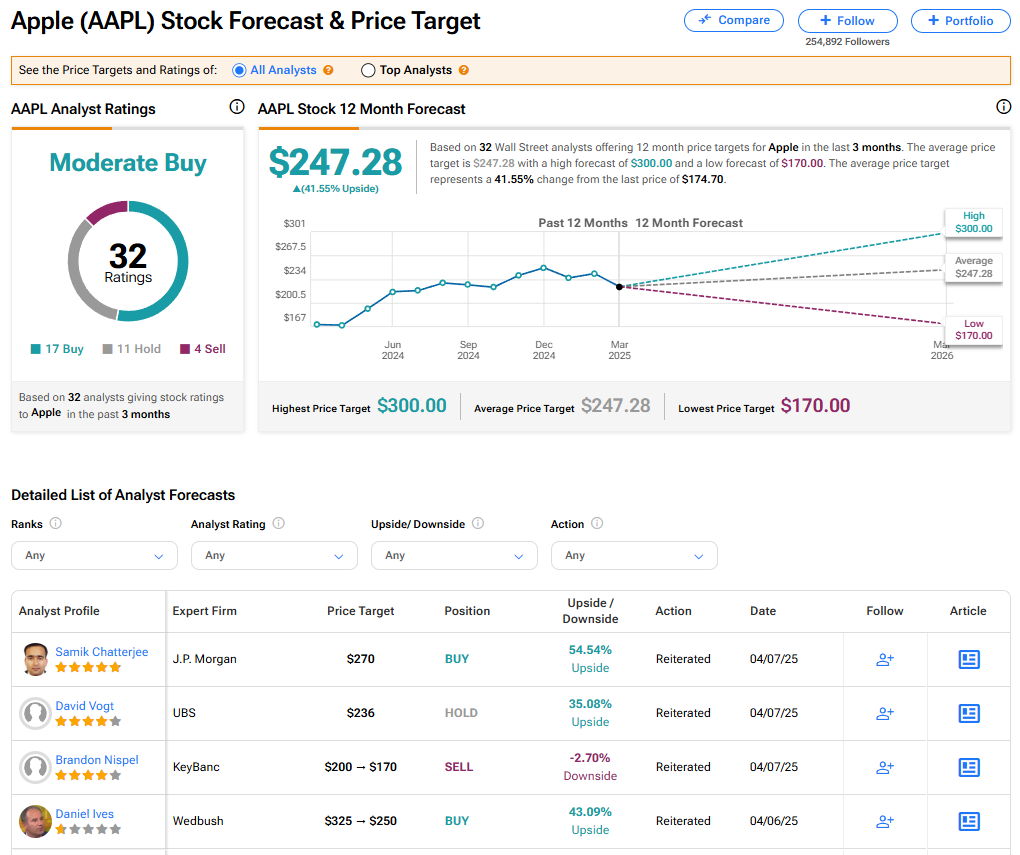
Apple and Nvidia are set to benefit from the exemption from tariffs on Chinese imported goods. This could lead to a potential boost to their stock prices.
Uncertainty for Other Companies
However, other companies may face uncertainty regarding the impact of tariffs on consumer demand and prices. Navigating the new tariff landscape will be challenging for many companies.
Conclusion
As the Trump administration announces exemptions from China tariffs for certain electronics, Apple and Nvidia are poised to reap significant benefits. The article highlights the impact of this decision on the tech industry, particularly on these two major players. By exempting electronics such as semiconductors and computer servers, the administration aims to alleviate the strain on American businesses and mitigate the effects of the ongoing trade tensions with China. This move is likely to boost Apple’s sales and Nvidia’s revenue, as they are major importers of these exempted electronics.
The significance of this development lies in its potential to ease the financial burden on American companies, which have struggled to adapt to the rising costs and complexities of international trade. The tariffs imposed on Chinese imports have led to a surge in prices, squeezing profit margins and hindering growth. By exempting these specific electronics, the administration is effectively providing a lifeline to the tech industry, which has been a key driver of American economic growth. As the industry continues to evolve, the implications of this decision will be far-reaching, with potential ripple effects on employment, innovation, and global competitiveness.
As the tech landscape continues to shift, one thing is clear: the exemption of electronics from China tariffs marks a significant turning point for Apple and Nvidia. This development will undoubtedly have far-reaching consequences, shaping the future of the tech industry and influencing the trajectory of American businesses. As the industry adapts to this new reality, one question remains: what’s next for the tech giants and the American economy? The answers will be revealed in the months and years to come, but one thing is certain: the stakes have been raised, and the outcome will be fascinating to watch.