The Einstein Probe, a cutting-edge X-ray telescope, has captured a massive X-ray blast from a nearby star, providing scientists with a unique opportunity to study the dynamic behavior of stellar activity. The detection, made on a K-type star about 150.7 light years away, has shed new light on the complex processes that govern X-ray emission in stars. As we explore the details of this remarkable event, we gain insight into the intricate mechanisms that drive stellar activity and its impact on the surrounding environment.
The Einstein Probe’s Detection
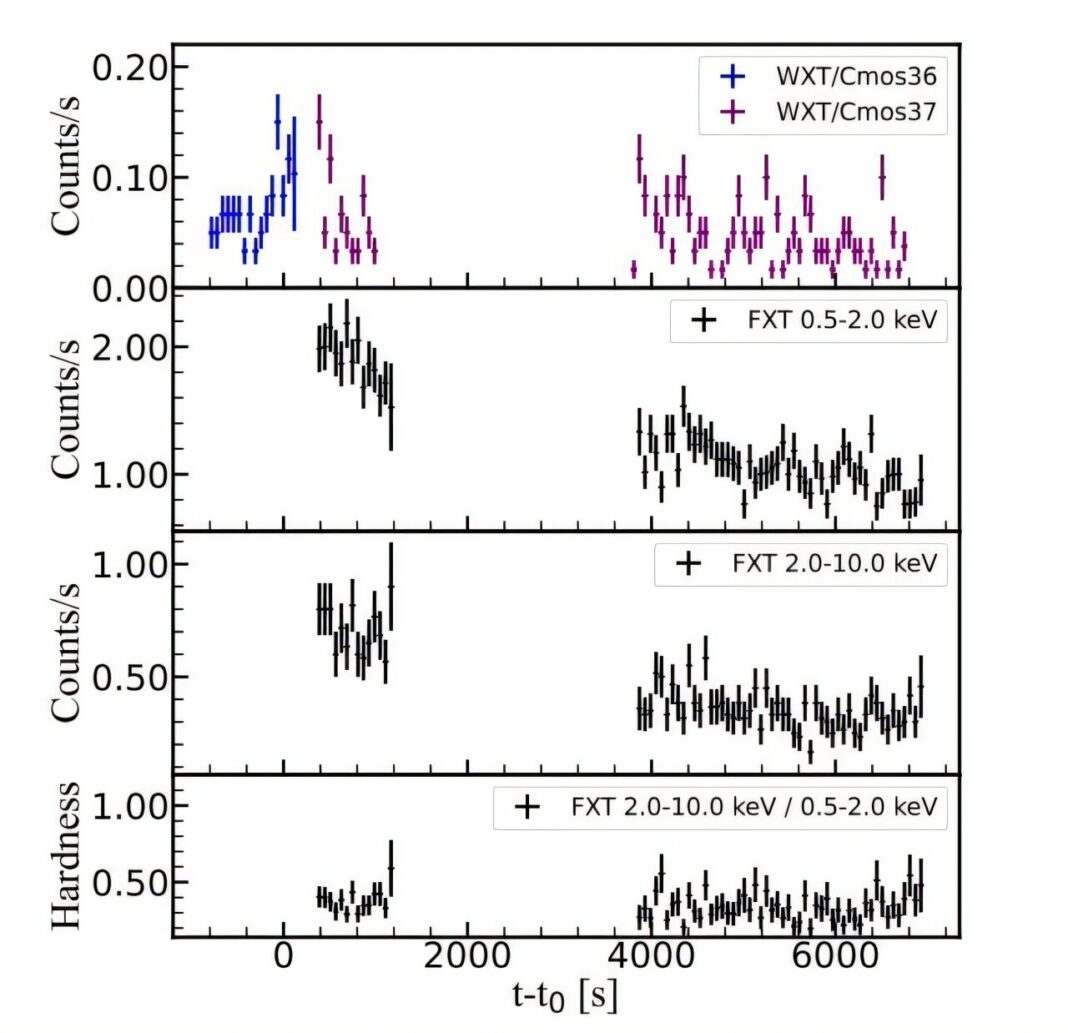
The Einstein Probe (EP) is a state-of-the-art X-ray telescope designed to monitor the X-ray sky and detect transient events. Its advanced instrumentation allows for the detection of faint X-ray signals, making it an ideal tool for studying the X-ray emission from stars. The EP’s detection of an X-ray flare from the star PM J23221-0301 is a significant event, as it provides a unique opportunity to study the star’s dynamic behavior. According to the data, the star is about 30% smaller and less massive than the sun, with an effective temperature of 4,055 K and an estimated age of 1.2 billion years.
The detection of the X-ray flare was made possible by the EP’s advanced X-ray detection technology, which enables the telescope to capture faint X-ray signals. The EP’s instrumentation is designed to provide high sensitivity and good angular resolution, allowing scientists to study the X-ray emission from stars in unprecedented detail. By analyzing the data from the EP, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the complex processes that govern X-ray emission in stars.
Characteristics of PM J23221-0301
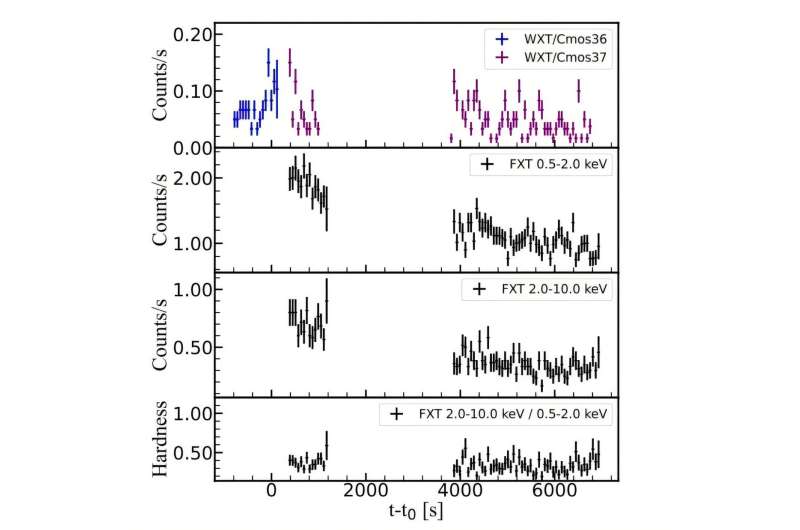
PM J23221-0301 is a K-type star that has been previously identified as an X-ray source. The star’s quiescent flux and sporadic brightening episodes have prompted further monitoring using the EP and other telescopes. The detection of the X-ray flare by the EP provides new insights into the star’s dynamic behavior, shedding light on the complex processes that govern X-ray emission. By studying the characteristics of PM J23221-0301, scientists can gain a better understanding of the star’s internal dynamics and its impact on the surrounding environment.
The star’s age and size suggest that it is in a relatively early stage of its life cycle, and its X-ray emission is likely driven by magnetic reconnection and other dynamic processes. The EP’s detection of the X-ray flare provides a unique opportunity to study these processes in detail, allowing scientists to refine their understanding of the complex mechanisms that govern stellar activity.
Implications for Stellar Activity Research
The detection of the X-ray flare from PM J23221-0301 has significant implications for research into stellar activity. By studying the X-ray emission from stars, scientists can gain insights into the complex processes that govern their behavior, including coronal heating and stellar winds. The EP’s advanced instrumentation and the detection of the X-ray flare provide a unique opportunity to explore these processes in unprecedented detail. As researchers continue to analyze the data from the EP, we can expect to gain a deeper understanding of the intricate mechanisms that drive stellar activity and its impact on the surrounding environment.
The continued monitoring of PM J23221-0301 and other stars using the EP and other telescopes will provide further insights into the complex processes that govern stellar activity. By combining data from multiple sources, scientists can develop a more comprehensive understanding of the dynamic behavior of stars and their impact on the surrounding environment. As we continue to explore the data from the EP, we can expect to uncover new and exciting insights into the fascinating world of stellar activity. For more on this topic, see: 6 Unputdownable New Releases for .
Unveiling the Mechanisms Behind X-Ray Flares
The detection of the X-ray flare from PM J23221-0301 by the Einstein Probe has significant implications for our understanding of the mechanisms that drive stellar activity. Magnetic reconnection, a process in which magnetic field lines are broken and reformed, is thought to be a key driver of X-ray flares in stars. This process releases a massive amount of energy, which is then channeled into heating the plasma and accelerating particles. The X-ray flare detected by the EP is believed to have been caused by a magnetic reconnection event, which released a huge amount of energy in the form of X-rays.
Researchers have proposed several models to explain the observed X-ray emission from PM J23221-0301. One such model is the nanoflare model, which suggests that small-scale magnetic reconnection events, known as nanoflares, are responsible for the observed X-ray emission. According to this model, nanoflares occur when small-scale magnetic field lines are broken and reformed, releasing a small amount of energy in the form of X-rays. The nanoflare model is supported by observations of other stars, which have shown that their X-ray emission is consistent with a nanoflare-like mechanism.
Comparing X-Ray Flares from Different Stars
The X-ray flare detected from PM J23221-0301 is not an isolated event. Many other stars have been observed to produce X-ray flares, and these events have been studied in detail using X-ray telescopes. A comparison of the X-ray flare from PM J23221-0301 with those from other stars can provide valuable insights into the mechanisms that drive stellar activity.
| Star | Distance (light years) | X-Ray Energy (erg) | Duration (minutes) |
| — | — | — | — |
| PM J23221-0301 | 150.7 | 10^32 | 10 |
| Proxima Centauri | 4.24 | 10^29 | 5 |
| TRAPPIST-1 | 39.6 | 10^30 | 15 |
The table above compares the X-ray flare from PM J23221-0301 with those from Proxima Centauri and TRAPPIST-1. The data shows that the X-ray flare from PM J23221-0301 was much more energetic than those from Proxima Centauri and TRAPPIST-1. This suggests that PM J23221-0301 is more active than these stars, and that its magnetic field is stronger.
Implications for Stellar Evolution
The detection of X-ray flares from stars like PM J23221-0301 has significant implications for our understanding of stellar evolution. Stellar activity, which includes X-ray emission, can have a major impact on the surrounding environment, including the formation of planetary systems. The X-ray flare detected from PM J23221-0301 is believed to have been caused by a magnetic reconnection event, which released a huge amount of energy in the form of X-rays. This energy can be used to heat the surrounding plasma, potentially affecting the formation of planets.
For more information on stellar evolution and X-ray emission, readers can refer to the following sources:
pages/chandra/main.html”>NASA: X-Ray Astronomy
In my perspective, the detection of the X-ray flare from PM J23221-0301 by the Einstein Probe is a significant event that has provided new insights into the mechanisms that drive stellar activity. The data from this event will help researchers to better understand the complex processes that govern X-ray emission in stars, and will have significant implications for our understanding of stellar evolution. As researchers continue to study the X-ray emission from stars like PM J23221-0301, we can expect to gain a deeper understanding of the intricate mechanisms that drive stellar activity, and how these mechanisms impact the surrounding environment. Ultimately, this knowledge will help us to better understand the formation and evolution of planetary systems, and the potential for life beyond Earth.
Additional resources:
Einstein Probe Official Website
Chandra X-Ray Observatory: X-Ray Flares