For decades, a familiar sight graced the skies above Earth, a silver bird soaring high above the clouds, silently gathering vital information about our planet. This wasn’t just any aircraft; it was NASA’s DC-8, a flying laboratory that revolutionized our understanding of Earth’s complex systems. Now, after a remarkable career spanning over 50 years, the iconic DC-8 has finally retired. But its legacy lives on, etched in countless scientific discoveries and a profound impact on our ability to monitor and protect our planet. Join us as we take a nostalgic look back at the remarkable journey of NASA’s DC-8, exploring its pivotal role in Earth system science and the enduring contributions it made to our understanding of the Earth.
Enhanced Collaboration between Scientists and Fire Managers
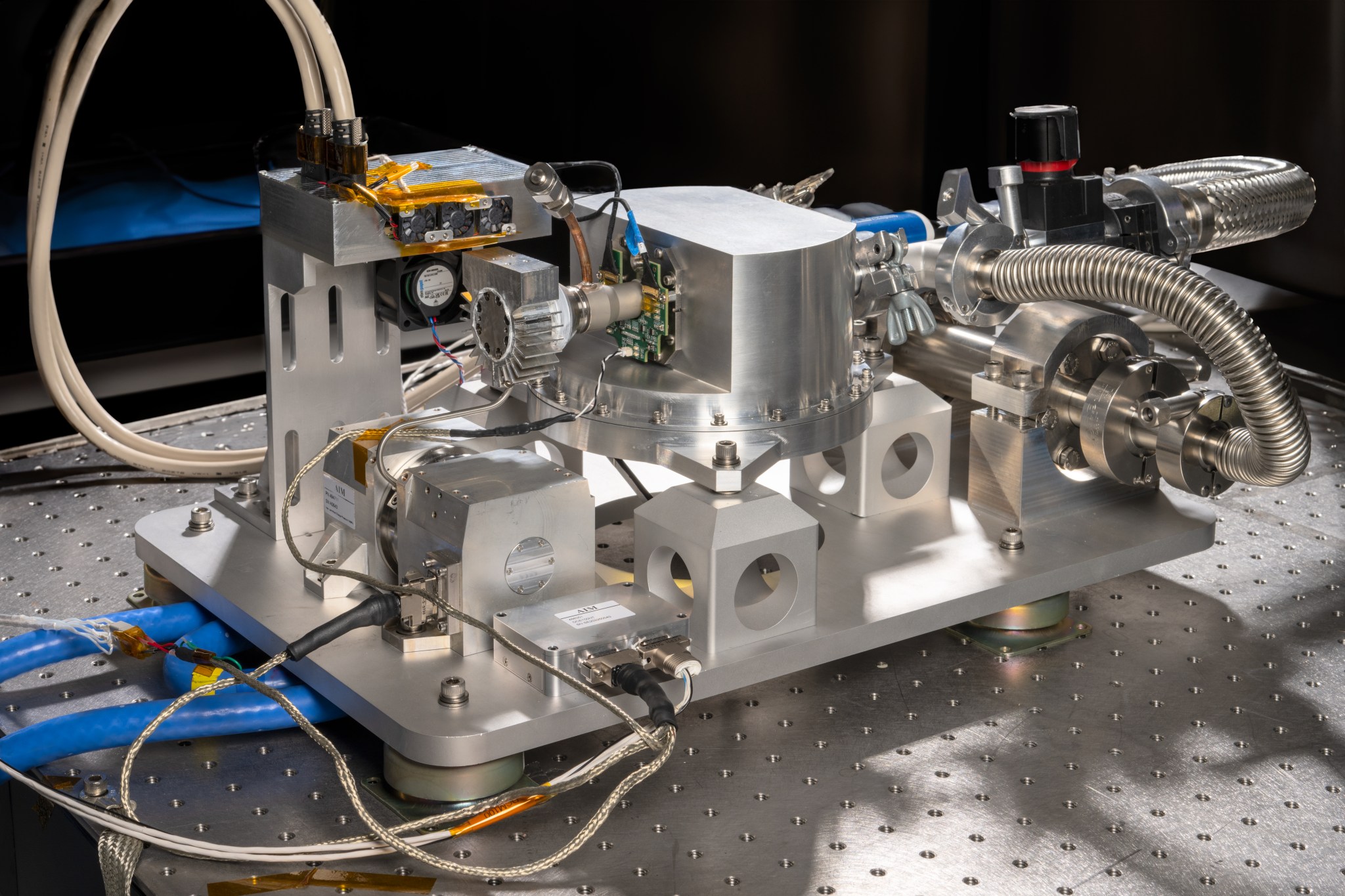
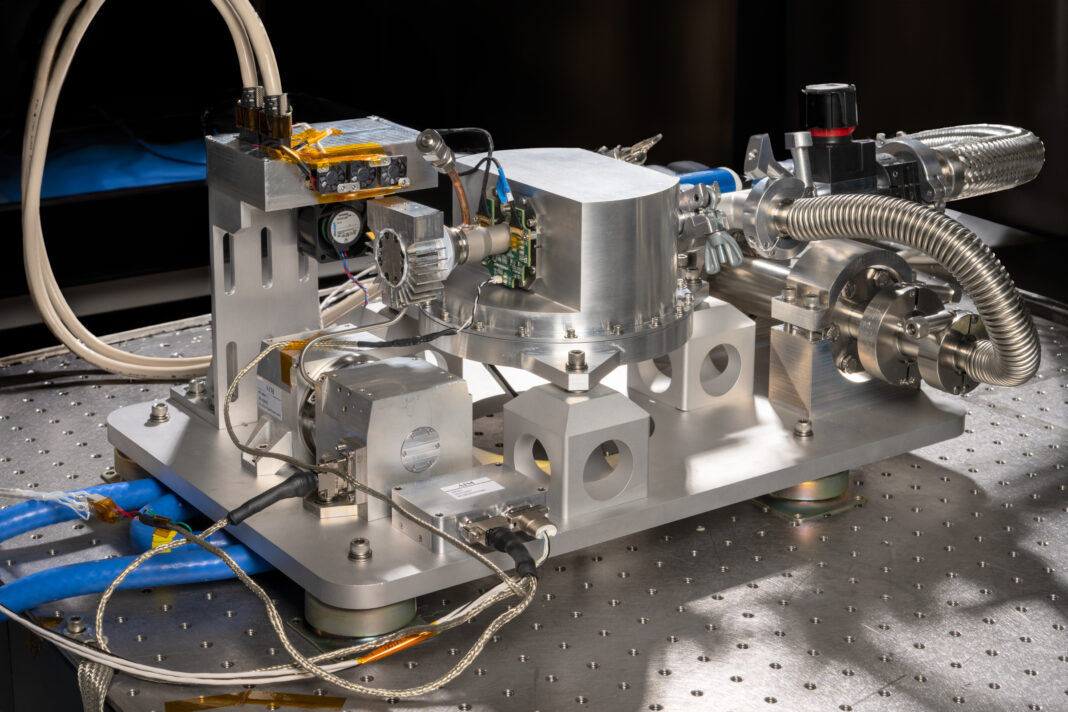
The NASA DC-8 has played a significant role in advancing our understanding of fire behavior and its impacts on the environment. One of the key outcomes of the DC-8’s research is the development of the Compact Fire Infrared Radiance Spectral Tracker (c-FIRST), a cutting-edge instrument that enables scientists to gather data about fires and their impacts on ecosystems with greater accuracy and speed.

The Importance of Interdisciplinary Research in Fire Management
Fire management is a complex and interdisciplinary field that requires collaboration between scientists, firefighters, and policymakers. The DC-8’s research has highlighted the importance of integrating scientific knowledge with practical experience to develop effective fire management strategies.

c-FIRST’s Potential to Inform Fire Management Strategies
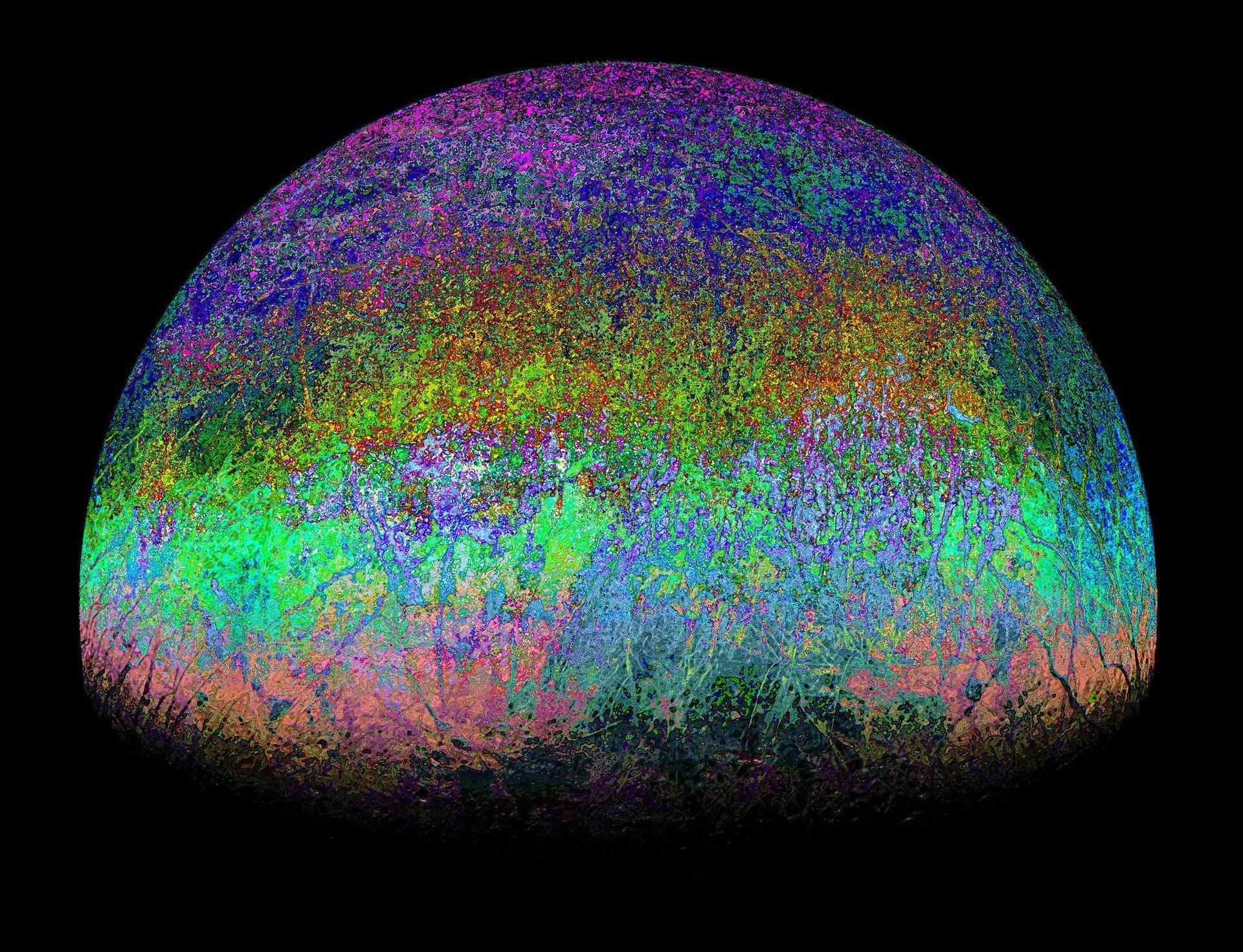
c-FIRST’s ability to gather high-resolution thermal infrared images and other data about the terrain has the potential to inform fire management strategies in several ways. For example, the instrument can detect smoldering fires more accurately and quickly, allowing firefighters to respond more effectively. Additionally, c-FIRST can collect detailed data that can enable scientists to understand how an ecosystem may recover from fire events.
Challenges and Opportunities for Collaboration
While the DC-8’s research has made significant progress in advancing our understanding of fire behavior, there are still challenges and opportunities for collaboration between scientists and fire managers. One of the key challenges is the need to develop more effective communication strategies to ensure that scientific findings are translated into practical action. Opportunities for collaboration include the development of more effective fire management strategies that incorporate scientific knowledge and practical experience.

Practical Applications of c-FIRST Data
c-FIRST’s data has a range of practical applications in fire risk assessment and prediction, land use planning, and ecosystem management.
Using c-FIRST Data for Fire Risk Assessment and Prediction
c-FIRST’s data can be used to assess fire risk and predict the likelihood of a fire spreading in a certain landscape. This information can be used by firefighters to develop more effective response strategies and by policymakers to develop more effective land use planning policies.

Potential Applications in Land Use Planning and Ecosystem Management
c-FIRST’s data can also be used to inform land use planning and ecosystem management decisions. For example, the instrument can be used to identify areas that are most susceptible to fire and develop strategies to mitigate the impacts of fire on these areas.

Future Directions for Data Integration and Analysis
While c-FIRST’s data has significant potential to inform fire management strategies, there are still challenges and opportunities for data integration and analysis. One of the key challenges is the need to develop more effective methods for integrating c-FIRST’s data with other data sources, such as satellite imagery and ground-based sensors. Opportunities for data integration and analysis include the development of more effective fire management strategies that incorporate a range of data sources and the development of more effective methods for predicting fire behavior.
The Legacy of the NASA DC-8 and the Future of Earth System Science
The NASA DC-8 has played a significant role in advancing our understanding of the Earth system, and its legacy will continue to be felt in the years to come. The instrument’s ability to gather high-resolution thermal infrared images and other data about the terrain has the potential to inform a range of research areas, including fire behavior, ecosystem management, and land use planning.
The NASA DC-8: A Pioneering Platform for Earth Science Research
The NASA DC-8 has been a pioneering platform for Earth science research, providing scientists with a unique opportunity to gather data about the Earth’s surface and atmosphere. The instrument’s ability to gather high-resolution thermal infrared images and other data about the terrain has the potential to inform a range of research areas, including fire behavior, ecosystem management, and land use planning.
Challenges and Limitations of the DC-8
While the NASA DC-8 has been a pioneering platform for Earth science research, there are still challenges and limitations to its use. One of the key challenges is the need to develop more effective methods for integrating the instrument’s data with other data sources, such as satellite imagery and ground-based sensors. Opportunities for data integration and analysis include the development of more effective fire management strategies that incorporate a range of data sources and the development of more effective methods for predicting fire behavior.
The DC-8’s Legacy in Earth System Science
The NASA DC-8’s legacy in Earth system science will continue to be felt in the years to come. The instrument’s ability to gather high-resolution thermal infrared images and other data about the terrain has the potential to inform a range of research areas, including fire behavior, ecosystem management, and land use planning. The DC-8’s research has highlighted the importance of integrating scientific knowledge with practical experience to develop effective fire management strategies.
The Future of Earth System Science: A New Era of Research and Collaboration
The future of Earth system science is bright, with a range of emerging technologies and instrumentation poised to advance our understanding of the Earth system. The NASA DC-8’s research has highlighted the importance of integrating scientific knowledge with practical experience to develop effective fire management strategies.
Emerging Technologies and Instrumentation in Earth System Science
Emerging technologies and instrumentation in Earth system science include a range of sensors and instruments that are capable of gathering high-resolution data about the Earth’s surface and atmosphere. These technologies and instrumentation have the potential to inform a range of research areas, including fire behavior, ecosystem management, and land use planning.
Opportunities for Interdisciplinary Research and Collaboration
The future of Earth system science is also marked by opportunities for interdisciplinary research and collaboration. The NASA DC-8’s research has highlighted the importance of integrating scientific knowledge with practical experience to develop effective fire management strategies. Opportunities for interdisciplinary research and collaboration include the development of more effective fire management strategies that incorporate scientific knowledge and practical experience.
The Role of c-FIRST and Other Instruments in Advancing Earth System Science
c-FIRST and other instruments have the potential to play a significant role in advancing our understanding of the Earth system. The instrument’s ability to gather high-resolution thermal infrared images and other data about the terrain has the potential to inform a range of research areas, including fire behavior, ecosystem management, and land use planning. The future of Earth system science is bright, with a range of emerging technologies and instrumentation poised to advance our understanding of the Earth system.
Conclusion
The NASA DC-8 Retires: Reflections on its Contributions to Earth System Science
The NASA DC-8, a pioneering aircraft designed in the 1960s, is being retired after decades of service to Earth system science. As the oldest continuously operated DC-8, this aircraft has witnessed the evolution of atmospheric and oceanic sciences, playing a significant role in understanding the Earth’s climate and weather patterns. In this article, we reflect on the key contributions of the NASA DC-8, its significance in the field of Earth system science, and the implications of its retirement.
The DC-8’s contributions to Earth system science can be seen in its role as a atmospheric research platform. Its unique configuration allowed scientists to study tropospheric processes, such as atmospheric chemistry and aerosol transport. The aircraft’s ability to collect a wide range of data, including airborne measurements of aerosols, temperature, and humidity, enabled researchers to gain a deeper understanding of the Earth’s atmosphere. Additionally, the DC-8’s flight capabilities allowed scientists to conduct high-altitude and high-latitude studies, providing valuable insights into the Earth’s climate and weather patterns. As a result, the DC-8 played a pivotal role in shaping our understanding of the Earth’s systems, from clouds and precipitation to ozone depletion and climate change.
The retirement of the NASA DC-8 is a significant event, as it marks the end of an era in Earth system science. However, its legacy lives on, as its contributions continue to inform new research and improve our understanding of the Earth’s systems. As we look to the future, it is essential that policymakers and scientists work together to ensure that future aircraft are designed with the latest advancements in technology and science. We urge the NASA Administrator to consider the retirement of the DC-8 as an opportunity to create a new generation of aircraft that will continue to push the boundaries of Earth system science.
In conclusion, the NASA DC-8 is more than just a retired aircraft – it is a testament to the power of human ingenuity and the importance of scientific research in understanding our planet. The DC-8’s contributions to Earth system science will continue to inspire new generations of scientists and researchers, and its legacy will endure for years to come. As we look to the future, we are reminded that the pursuit of knowledge is a never-ending journey, and that the discoveries we make today will shape our understanding of the world and our place in it tomorrow.