## Unleashing the Power of Innovation: How Rare Disease Research is Pushing the Boundaries of Clinical Trials
Imagine a world where the challenges of diagnosing and treating rare diseases are met with cutting-edge technology and innovative clinical trial designs. This isn’t a futuristic fantasy; it’s the reality unfolding right now, driven by a dedicated community of researchers and the unwavering hope of patients and families. Rare disease research is not just about finding cures; it’s a catalyst for revolutionizing the entire landscape of clinical trials, ushering in an era of personalized medicine and faster, more efficient breakthroughs.

Consolidation in the EDC Market
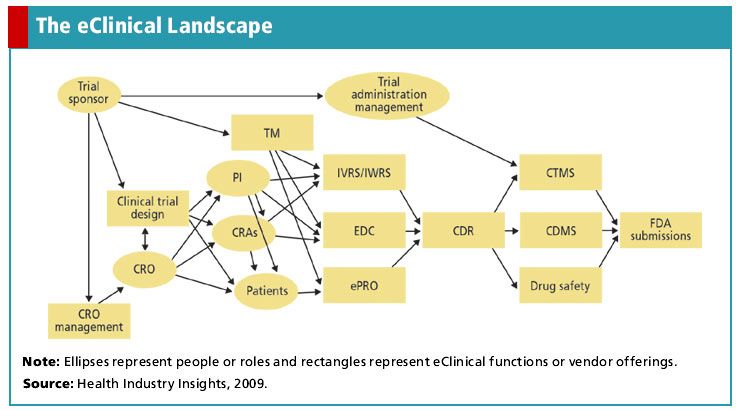
The Electronic Data Capture (EDC) market is undergoing significant changes, with predictions of further consolidation in the near future. According to Alan S. Louie, PhD, and author of the Health Industry Insights report, the EDC market is becoming a mature technology, leading to decreased competition among vendors. This maturity, coupled with the adoption of CDISC standards, has resulted in easier interoperability and a less competitive market.
Recent M&A activity in the EDC space supports this prediction. In 2008, notable acquisitions included Parexel’s purchase of ClinPhone, BioImaging’s acquisition of Phoenix Data Systems (now known as BioClinica), and Medidata’s purchase of Fast Track. More recently, OmniComm Systems purchased ERT’s EDC product suite, and Covance sold its IVRS/IWRS services to Phase Forward. These acquisitions demonstrate the trend of consolidation in the EDC market, with vendors seeking to expand their offerings and compete with tier-one players.

Predictions for Further Consolidation
Steve Johnson, COO of OmniComm Systems, agrees with Louie’s prediction of further consolidation in the EDC market. Johnson believes that future consolidations will focus on acquisitions of products that complete a company’s offerings to a full eClinical suite. This will enable vendors to provide a comprehensive software product that meets the needs of clients, rather than having them seek out different products to plug into the system.
The implications of this consolidation for buyers and vendors in the EDC market are significant. Vendors must be aware of the trend towards eClinical and the need to provide a comprehensive software product that meets the needs of clients. Buyers, on the other hand, must be aware of the potential for consolidation and the impact it may have on their current and future software needs.
The Move Towards Web-Based Solutions
The improved security and performance of the Internet have played a significant role in the adoption of Web-based EDC solutions. According to Louie, the major benefits of Web-based solutions include the elimination of the need to manage software on-site and the ability to serve distributed trials or global trial data needs.
Web-based solutions have brought EDC to maturity and are driving the adoption of eClinical. As Johnson explained, “It is the improved security and the performance of the Internet in the past couple years that explains why EDC has taken off.” The use of Web-based solutions has also enabled the development of more comprehensive software products that meet the needs of clients.

Benefits of Web-Based EDC Solutions
The benefits of Web-based EDC solutions are numerous. They include:
- Elimination of the need to manage software on-site
- Ability to serve distributed trials or global trial data needs
- Improved security and performance
- Increased flexibility and scalability
These benefits have made Web-based EDC solutions an attractive option for clients, and vendors are responding by developing more comprehensive software products that meet their needs.
Practical Applications and Implications
The Future of eClinical and Rare Disease Research
Rare disease research is a unique and challenging field, with competing priorities among researchers, difficulty in diagnosing and treating patients, and defining endpoints due to varying symptoms. According to Derek Ansel, vice president, therapeutic strategy lead, rare disease, Worldwide Clinical Trials, the use of technology and artificial intelligence (AI) has the potential to address some of these challenges and improve rare disease research.
Ansel believes that rare disease research leads the technology and innovation front, with the use of AI and other technologies having the potential to revolutionize the field. The use of AI, for example, can help diagnose patients faster by analyzing images of children with dysmorphic features, or by linking approved drugs to support and treat patients who otherwise would not have access to them.
The impact of eClinical on the future of rare disease research will be significant. eClinical will enable researchers to collect and manage data more efficiently, improve collaboration and communication among stakeholders, and accelerate the development of new treatments. The practical implications for researchers, clinicians, and patients will be profound, with the potential for improved outcomes and increased access to effective treatments.
The Importance of Collaboration and Innovation
Global collaboration and innovation are essential for advancing rare disease research. According to Ansel, increasing global collaboration across stakeholders is critical, as rare disease research is challenging due to the varying symptoms and difficulty in diagnosing and treating patients. The use of technology and AI can facilitate collaboration and innovation, enabling researchers to share data and knowledge more effectively.
Role of Technology in Facilitating Collaboration and Innovation
Technology plays a critical role in facilitating collaboration and innovation in rare disease research. The use of Web-based solutions, for example, enables researchers to share data and collaborate more effectively, regardless of their location. The use of AI and other technologies can also help analyze large datasets and identify patterns that may not be apparent to human researchers.
The practical implications of collaboration and innovation in rare disease research are significant. By working together and sharing knowledge and data, researchers can accelerate the development of new treatments and improve outcomes for patients. The use of technology and AI can facilitate this process, enabling researchers to collaborate more effectively and make new discoveries that may not have been possible otherwise.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, the EDC market is undergoing significant changes, with predictions of further consolidation and a move towards Web-based solutions. The use of technology and AI has the potential to revolutionize rare disease research, enabling researchers to collect and manage data more efficiently, improve collaboration and communication among stakeholders, and accelerate the development of new treatments.
Summary of Key Points and Takeaways
The key points and takeaways from this discussion include:
- The EDC market is becoming a mature technology, leading to decreased competition among vendors
- Further consolidation is predicted in the EDC market, with a focus on acquisitions of products that complete a company’s offerings to a full eClinical suite
- Web-based solutions have brought EDC to maturity and are driving the adoption of eClinical
- Rare disease research leads the technology and innovation front, with the use of AI and other technologies having the potential to revolutionize the field
Recommendations for future research and innovation in rare disease research include increasing global collaboration across stakeholders, leveraging technology and AI to facilitate collaboration and innovation, and accelerating the development of new treatments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the realm of rare disease research has emerged as a beacon of innovation, driving technological advancements and pushing the boundaries of medical possibilities. Through the applied clinical trials, researchers have been able to unravel the complexities of these enigmatic conditions, yielding novel insights into the human body’s intricate mechanisms. The article has delved into the transformative power of rare disease research, highlighting its far-reaching implications for the broader healthcare landscape. From the development of precision medicine to the acceleration of gene therapy, the breakthroughs emanating from this field have the potential to reshape the future of healthcare.
As we look to the future, it is clear that rare disease research will continue to occupy a vital position at the forefront of technological innovation. With the increasing adoption of AI, machine learning, and genomics, the pace of discovery is poised to accelerate, unlocking new avenues for treatment and therapy. Moreover, the emphasis on collaboration and data sharing will be crucial in harnessing the collective power of the scientific community, driving progress, and improving patient outcomes. Ultimately, the significance of rare disease research extends beyond the rare disease community, holding the key to unlocking cures for a wide range of debilitating conditions.
As we stand at the threshold of this new era of medical innovation, it is imperative that we continue to invest in and support rare disease research. By doing so, we will not only be improving the lives of millions affected by these conditions but also paving the way for a future where the boundaries of human health are redefined. As we forge ahead, let us remember that the pursuit of medical breakthroughs is not merely a scientific endeavor, but a moral imperative – one that demands our collective commitment to creating a world where no one is left behind, and every life is valued.
