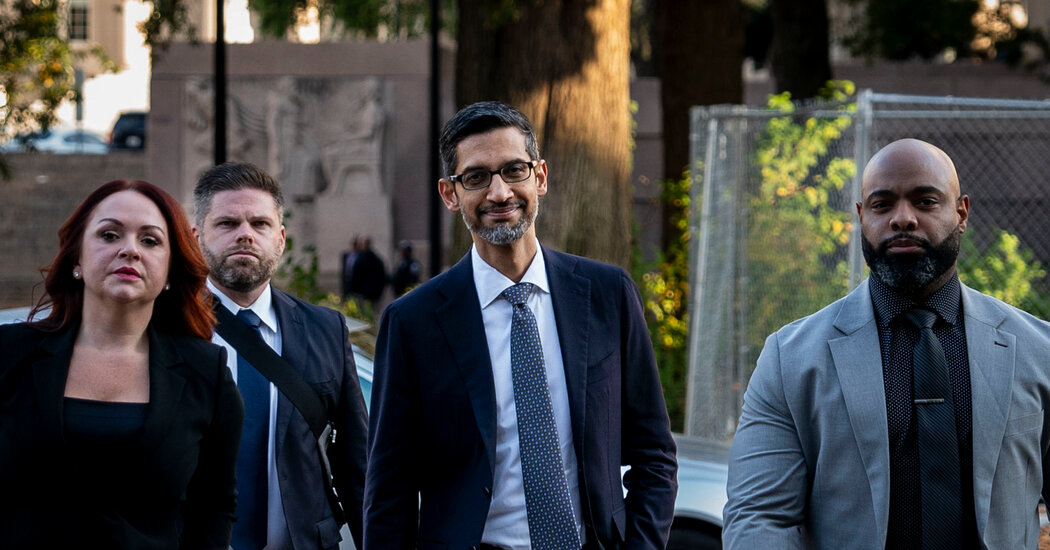
## Google’s on the ropes: Can Big Tech giants be tamed?
Silicon Valley’s behemoth, Google, is facing a fight for its future. A landmark proposal to break up the tech giant, spearheaded by US lawmakers, has sent shockwaves through the industry, pitting Google’s CEO against the very foundations of American antitrust law.
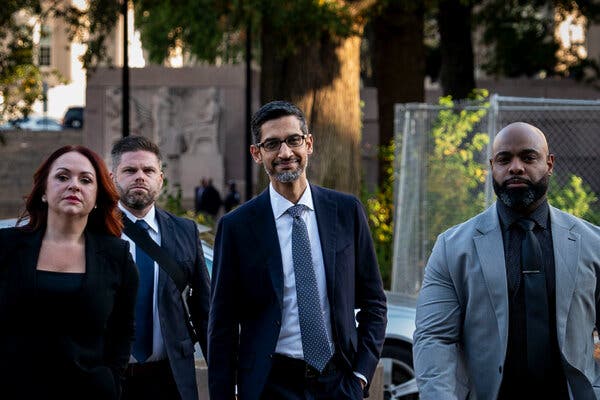

In a stark warning, Google’s Sundar Pichai has declared that dismantling the company would cripple its ability to innovate and compete, throwing the future of internet search and countless other services into uncertainty. But is this a genuine plea for survival or a shrewd maneuver to deflect criticism from a company wielding immense power?

Impact on Google’s Workforce and the Job Market in the Tech Industry

Google’s Chief Executive, Sundar Pichai, recently testified that a government proposal to break up the company would hobble the business, as he aimed to stave off drastic changes to fix an illegal monopoly in online search. This development has sparked concerns about the potential impact on Google’s workforce and the job market in the tech industry.
According to a report by Glassdoor, Google has a workforce of over 150,000 employees globally, with a significant proportion of them being software engineers, product managers, and data scientists. A breakup of the company could lead to significant job losses, particularly among these critical roles.
Furthermore, a breakup could also lead to a decline in innovation and investment in research and development, as Google would need to allocate resources to maintain multiple separate entities. This could have a ripple effect on the broader tech industry, as Google’s competitors might also be forced to reduce their investments in R&D to stay competitive.
- Job losses: A breakup could lead to significant job losses, particularly among software engineers, product managers, and data scientists.
- Decline in innovation: A breakup could lead to a decline in innovation and investment in research and development, as Google would need to allocate resources to maintain multiple separate entities.
- Impact on competitors: A breakup could also lead to a decline in innovation and investment among Google’s competitors, as they would need to reduce their investments in R&D to stay competitive.

Implications for Economic Growth and the Overall Economy
The implications of a Google breakup for economic growth and the overall economy are far-reaching and complex. On one hand, a breakup could lead to increased competition, which could drive innovation and improve consumer choice.
On the other hand, a breakup could also lead to a decline in investment in R&D, which could have a negative impact on economic growth. According to a report by the National Bureau of Economic Research, a decline in R&D investment can lead to a decline in productivity growth, which can have a negative impact on economic growth.
Furthermore, a breakup could also lead to a decline in Google’s market value, which could have a negative impact on the broader economy. According to a report by Bloomberg, Google’s market value has been a significant contributor to the overall market value of the tech industry.
- Increased competition: A breakup could lead to increased competition, which could drive innovation and improve consumer choice.
- Decline in R&D investment: A breakup could also lead to a decline in investment in R&D, which could have a negative impact on economic growth.
- Decline in market value: A breakup could also lead to a decline in Google’s market value, which could have a negative impact on the broader economy.
Alternative Solutions and Reforms
There are alternative solutions to a breakup that could address Google’s market power while minimizing the negative impacts on the company’s workforce and the broader economy.
One such solution is regulatory reforms, which could be implemented to address Google’s market power while allowing the company to continue innovating and investing in R&D. According to a report by the Brookings Institution, regulatory reforms could be implemented to address issues such as data portability, interoperability, and competition promotion.
Another solution is increased competition, which could be achieved through policies such as promoting competition in the tech industry, encouraging innovation, and protecting consumer choice. According to a report by the Electronic Frontier Foundation, increased competition could be achieved through policies such as breaking up large tech companies, promoting competition in the cloud computing market, and protecting consumer choice in the digital market.
- Regulatory reforms: Regulatory reforms could be implemented to address Google’s market power while allowing the company to continue innovating and investing in R&D.
- Increased competition: Increased competition could be achieved through policies such as promoting competition in the tech industry, encouraging innovation, and protecting consumer choice.
The Regulatory and Policy Context
Antitrust Laws and Enforcement
Antitrust laws and enforcement play a critical role in regulating the tech industry and addressing issues such as market power, competition, and consumer protection.
According to a report by the Federal Trade Commission, antitrust laws and enforcement are critical in promoting competition, protecting consumer choice, and promoting innovation in the tech industry.
However, enforcing antitrust laws in the tech industry is complex and challenging. According to a report by the Harvard Business Review, enforcing antitrust laws in the tech industry requires a deep understanding of the industry, its players, and its dynamics.
- Antitrust laws: Antitrust laws and enforcement play a critical role in regulating the tech industry and addressing issues such as market power, competition, and consumer protection.
- Enforcement challenges: Enforcing antitrust laws in the tech industry is complex and challenging.
The Regulatory and Policy Context
International Perspectives and Competition
International perspectives and competition play a critical role in regulating the tech industry and addressing issues such as market power, competition, and consumer protection.
According to a report by the World Trade Organization, international trade agreements and regulations play a critical role in promoting competition, protecting consumer choice, and promoting innovation in the tech industry.
However, international regulatory approaches can vary significantly, and a Google breakup could have different implications depending on the country or region. According to a report by the European Commission, a Google breakup could have significant implications for the European tech industry, including increased competition and innovation.
- International trade agreements: International trade agreements and regulations play a critical role in promoting competition, protecting consumer choice, and promoting innovation in the tech industry.
- Divergent regulatory approaches: International regulatory approaches can vary significantly, and a Google breakup could have different implications depending on the country or region.
Future Directions and Policy Reforms
Potential Policy Reforms and Regulatory Changes
Potential policy reforms and regulatory changes could address Google’s market power while minimizing the negative impacts on the company’s workforce and the broader economy.
One such reform is the creation of a new regulatory body to oversee the tech industry, which could be responsible for enforcing antitrust laws, promoting competition, and protecting consumer choice. According to a report by the Brookings Institution, a new regulatory body could be created to address issues such as data portability, interoperability, and competition promotion.
Another reform is the implementation of policies such as data protection, consumer protection, and competition promotion, which could be achieved through regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Competition and Markets Authority (CMA). According to a report by the Electronic Frontier Foundation, policies such as data protection, consumer protection, and competition promotion could be achieved through regulations such as the GDPR and the CMA.
- New regulatory body: A new regulatory body could be created to oversee the tech industry and address issues such as data portability, interoperability, and competition promotion.
- Policies and regulations: Policies such as data protection, consumer protection, and competition promotion could be achieved through regulations such as the GDPR and the CMA.
Conclusion
Conclusion: The Ongoing Antitrust Debate and Google’s Future
The recent proposal to break up Google, as discussed in The New York Times, has sparked a heated debate about the tech giant’s dominance in the market. Sundar Pichai, Google’s CEO, has emphasized that such a breakup would severely hinder the company’s ability to innovate and compete, potentially leading to a decline in services and benefits for consumers. This argument is rooted in the company’s sheer scale and complexity, with various divisions and subsidiaries that work in tandem to provide a seamless user experience. The article highlights the intricacies of the proposal, including concerns about the impact on Alphabet, Google’s parent company, and the potential for a fragmented market.
The significance of this discussion extends far beyond Google’s walls, as it touches on the broader topic of antitrust regulations and their implications for the tech industry. The proposed breakup has sparked concerns about the potential for a chilling effect on innovation, as companies may become less willing to invest in research and development if they fear being dismantled. This raises important questions about the balance between promoting competition and encouraging growth in the digital landscape. As the debate continues, it is essential to consider the long-term implications of such a decision and how it may shape the future of the tech industry.
As the antitrust debate rages on, one thing is clear: the decision to break up Google will have far-reaching consequences that will impact not just the company, but the entire tech ecosystem. The fate of Google’s various divisions, from Google Search to Google Maps, hangs in the balance, and the potential loss of innovation and progress is a sobering prospect. Ultimately, the question remains: will regulators prioritize breaking up Google or fostering a competitive environment that incentivizes growth and innovation? Only time will tell, but one thing is certain: the future of Google and the tech industry hangs precariously in the balance.
