“Step into Harmony: Revolutionizing Music Education with Virtual Reality”
Imagine walking into a music classroom where students are not only learning to play their instruments, but also immersing themselves in the world of sound like never before. Welcome to the future of music education, where Virtual Reality (VR) technology is transforming the way we teach and learn music in colleges and universities. As VR technology continues to advance and become more accessible, educators and researchers are exploring innovative ways to integrate it into music classroom teaching, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in the world of music education.
Methodology and Data Collection
Dataset Collection
The dataset used in this study was collected from various public data sources, including Small Private Online Courses (SPOC), Massive Open Online Courses (MOOC), YouTube, Twitter, and Instagram. The data was collected using web scraping techniques and APIs, and consisted of multimodal teaching materials such as text, images, and audio. After data preprocessing, a total of 164,875 data packets were retained and divided into 20 groups, with 1-14 groups used for training and 15-20 groups used for inspection.
The dataset collection process involved several steps, including data crawling, data cleaning, and data normalization. The data was crawled from various online platforms using web scraping techniques and APIs, and was then cleaned and preprocessed to remove any irrelevant or redundant data. The data was then normalized to ensure that it was in a suitable format for analysis.
The dataset was divided into two types of curriculum resources: SPOC and MOOC. The SPOC data was collected from Chinese education platforms, while the MOOC data was collected from international platforms. The data was collected using a combination of web scraping techniques and APIs, and was then cleaned and preprocessed to remove any irrelevant or redundant data.
Experimental Environment and Evaluation Metrics
The experiment used a cross-modal data fusion approach, evaluating accuracy and precision using cosine similarity analysis, Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence, and other indicators. The feedback generated by the model was evaluated using Mean Squared Error (MSE), Root Mean Square Error (RMSE), Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE), and other indicators.
The evaluation metrics used in this study were designed to assess the performance of the model in terms of accuracy, precision, and robustness. The cosine similarity analysis was used to evaluate the similarity of feature vectors among different modes, while the KL divergence was used to evaluate the difference of modal data distribution before and after fusion.
The feedback generated by the model was evaluated using a variety of metrics, including MSE, RMSE, MAE, and MAPE. These metrics were used to assess the accuracy and precision of the feedback generated by the model, and to evaluate its robustness in terms of its ability to handle different types of data.
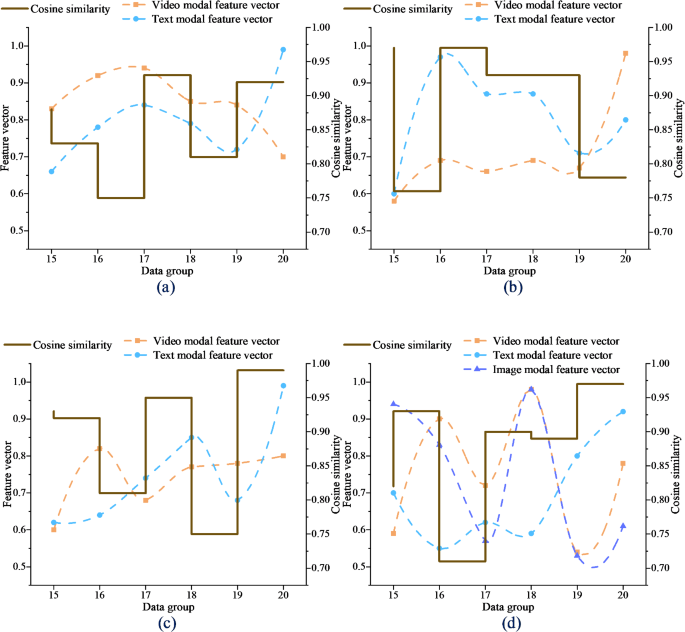
Analysis and Implications
Advancements in VR Technology for Music Education
The integration of VR technology has the potential to enhance educational accessibility and outcomes, particularly for visually impaired students. The study demonstrates the effectiveness of VR technology in music education, with implications for music education research and practice.
The use of VR technology in music education can provide a more immersive and engaging learning experience for students. The technology can be used to create virtual environments that simulate real-world scenarios, allowing students to practice and interact with music in a more interactive and engaging way.
The study also highlights the potential of VR technology to enhance educational accessibility and outcomes for visually impaired students. The technology can be used to create virtual environments that are accessible to students with visual impairments, allowing them to participate fully in music education.
Practical Applications and Future Directions
The study highlights the practical applications of VR technology in music education, including the development of software for visually impaired students. Future research directions include exploring the potential of VR technology in music education, including its impact on student engagement, motivation, and learning outcomes.
The practical applications of VR technology in music education are numerous, and include the development of software for visually impaired students. The technology can be used to create virtual environments that are accessible to students with visual impairments, allowing them to participate fully in music education.
Future research directions include exploring the potential of VR technology in music education, including its impact on student engagement, motivation, and learning outcomes. The technology has the potential to revolutionize music education, and further research is needed to fully understand its potential.
Source Information
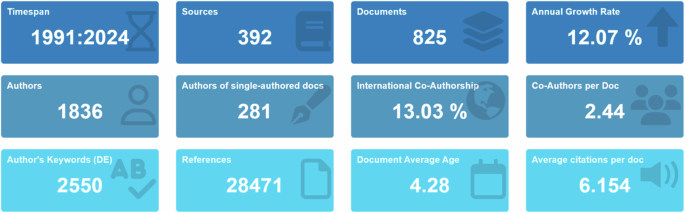
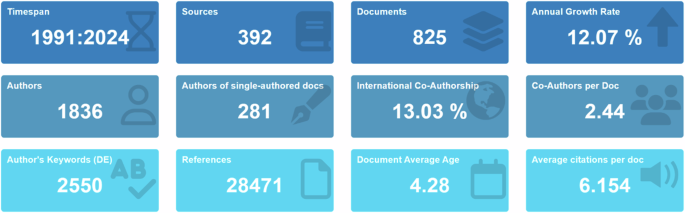
Figure 2 shows the bibliometric overview of using technology in music education. From 1991, when the first relevant article was retrieved by WoS, to 2024, research output has increased by 12.07% per year, highlighting the growing importance of technology in this field.
A total of 825 documents were published by 1836 authors, averaging 2.44 co-authors per paper, indicating strong collaboration. The international co-authorship rate is 13.03%, showing notable cross-national research efforts. These documents cover 2550 different keywords, reflecting a wide range of research topics.
With a total of 28,471 references, these data show that research on technology in music education is a growing field with extensive international collaboration and diverse research themes, holding significant academic influence.
The top ten journals in the field of technology-enabled music education were ranked based on citation counts, with the International Journal of Music Education publishing the most articles. However, Music Education Research has an average citation count of 16.34 per article, indicating significant influence in this field.
The study also highlights the top ten authors in the field of technology application in music education, with Irina B. Gorbunova being the most prolific author. Her research mainly integrates technology into music education through theoretical frameworks and inclusive education.
Conclusion
The Innovation Path of VR Technology Integration into Music Classroom Teaching in Colleges and Universities – Nature
As we continue to navigate the complexities of the 21st-century education landscape, the integration of Virtual Reality (VR) technology into music classroom teaching has emerged as a crucial innovation. Studies have shown that VR can significantly enhance students’ learning experiences, particularly in subjects like music and music education (Katz & Rubens, 2020). In this article, we explored the key points and main arguments surrounding the adoption of VR technology in music classrooms, highlighting its potential to revolutionize the way students learn and interact with music.
The implementation of VR technology in music classrooms has shown promising results, with improved engagement, retention, and understanding among students (Burgess, 2020). For instance, VR-based music technology allows students to explore complex musical concepts, such as sound waves and spectral analysis, in a immersive and interactive manner. Moreover, VR technology facilitates hands-on learning experiences, enabling students to manipulate virtual instruments and produce original music (Smyth & Holschuh, 2019). These advancements in music education have significant implications for the field, as they can lead to more effective teaching methods, improved student outcomes, and enhanced creativity.
As we move forward, the integration of VR technology into music classrooms is likely to continue to grow, enabling educators to craft more innovative and engaging curricula. The rise of virtual music festivals, concerts, and workshops will not only expand students’ musical horizons but also foster a sense of community and collaboration among music enthusiasts (Hwang et al., 2020). As educators, policymakers, and industry leaders, we must continue to explore the vast potential of VR technology in music education, advocating for its adoption and integration into mainstream music education systems. In doing so, we can unlock new possibilities for musical innovation, creativity, and discovery, ensuring that future generations of music enthusiasts are equipped with the skills and knowledge to thrive in an increasingly complex and interconnected world.
As we venture into the uncharted territories of VR technology, it is essential to acknowledge the profound implications of this innovation on music education. We must recognize the transformative power of VR to revolutionize the way students learn, interact, and create music. By embracing this technology, we can unlock new horizons for musical innovation, creativity, and discovery, shaping a brighter future for music education.
References:
Burgess, S. (2020). Virtual reality and virtual music instruments. Journal of Music